When you are applying to professional schools, it is important to showcase that you have the qualities that the program is looking for. One way to do this is by highlighting your CanMEDS roles. Each of the seven roles can be demonstrated through your academic and extracurricular experiences. In this blog post, we will discuss how you can make a strong application for medical school or dental school by showcasing your CanMEDS skills!
What are the CanMEDS Roles?
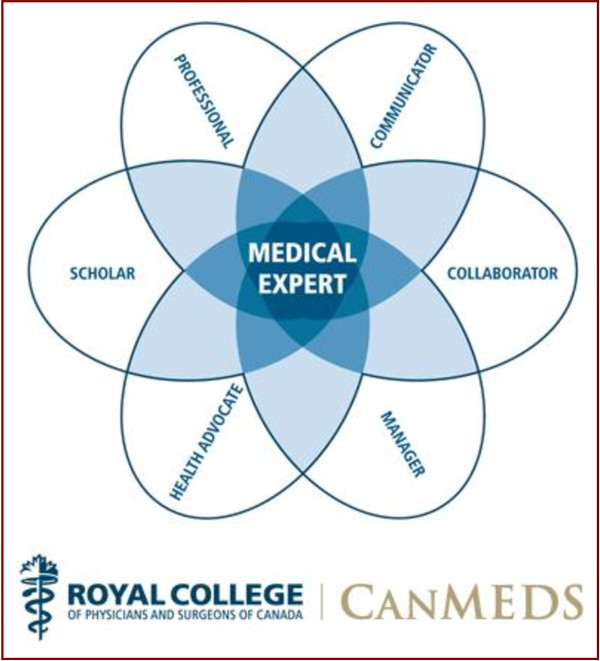
The CanMEDS roles were developed by the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada as a way to describe the competencies that all physicians should possess to effectively meet the health care needs of the people they serve. It is a framework for improving patient care by enhancing physician training. CanMEDS’s main purpose is to define the necessary competencies for all areas of medical practice and provide a comprehensive foundation for medical education and practice in Canada.
Since its formal adoption by the Royal College in 1996, CanMEDS has become the most widely accepted and applied physician competency framework in the world. It reflects the work of hundreds of Royal College Fellows and volunteers and is based on empirical research, sound education principles and broad stakeholder consultation. Renewal is key to the CanMEDS Framework’s ongoing success, which is why it has been updated twice since it was developed — in 2005 and again in 2015.
A competent physician seamlessly integrates the competencies of all seven CanMEDS roles listed below, as taken from the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada:
- Medical Expert: As Medical Experts, physicians integrate all of the CanMEDS Roles, applying medical knowledge, clinical skills, and professional values in their provision of high-quality and safe patient-centred care. Medical Expert is the central physician Role in the CanMEDS Framework and defines the physician’s clinical scope of practice.
- Communicator: As Communicators, physicians form relationships with patients and their families that facilitate the gathering and sharing of essential information for effective health care.
- Collaborator: As Collaborators, physicians work effectively with other health care professionals to provide safe, high-quality, patient-centred care
- Leader: As Leaders, physicians engage with others to contribute to a vision of a high-quality health care system and take responsibility for the delivery of excellent patient care through their activities as clinicians, administrators, scholars, or teachers.
- Health Advocate: As Health Advocates, physicians contribute their expertise and influence as they work with communities or patient populations to improve health. They work with those they serve to determine and understand needs, speak on behalf of others when required, and support the mobilization of resources to effect change.
- Scholar: As Scholars, physicians demonstrate a lifelong commitment to excellence in practice through continuous learning and by teaching others, evaluating evidence, and contributing to scholarship.
- Professionalism: As Professionals, physicians are committed to the health and well-being of individual patients and society through ethical practice, high personal standards of behaviour, accountability to the profession and society, physician-led regulation, and maintenance of personal health.
CanMEDS Roles and Professional School Applications
Why do CanMEDS matter in Professional School Applications?
The CanMEDS roles are important for professional school applications because they provide a framework for understanding the expectations of physicians. They also demonstrate the commitment of physicians to the health and well-being of their patients and communities. As such, applicants who can show that they understand and can articulate the CanMEDS roles will be at an advantage in the admissions process.
In addition, applicants who can demonstrate that they have experience related to the CanMEDS roles will also be at an advantage. For example, if an applicant has experience working on a health advocacy project, this will show that they have the skills and commitment required for the role of physician advocate. Similarly, if an applicant has experience conducting scholarly research, this will demonstrate their ability to contribute to the advancement of healthcare.
CanMEDS Roles do Not Need to be Demonstrated in a Healthcare Setting
It is important to note that the CanMEDS roles do not need to be demonstrated in a healthcare setting. For example, an applicant who has experience working on a political campaign would have the skills required for the role of a health advocate. Similarly, an applicant who has experience conducting research in another field would have the ability to contribute to the advancement of healthcare.
Even something as simple as being a camp counsellor can show that an applicant has the skills required for the role of communicator. Camp counsellors need to be able to communicate effectively with both children and adults, as well as being able to manage a team of people. This experience can be used to demonstrate an understanding of the CanMEDS role of communicator.
The bottom line is that it isn’t what you do that professional schools care about, it is how you do it and what you learned from it. Applicants who can show that they have the skills and qualities required for the CanMEDS roles, regardless of where they acquired those skills, will be at an advantage in the admissions process.
So How do I Implement CanMEDS Roles Into my Application?
If you are still wondering how to implement the CanMEDS roles into your professional school application, don’t worry, we have some tips for you!
First, take the time to understand each and every CanMEDS role. It is important that you can not only identify the roles but also explain what each one entails. It is only through thoroughly understanding the CanMEDS roles that you will be able to effectively demonstrate how you meet them. Scroll down for a more comprehensive overview of each role.
Second, take some time to reflect on your past experiences and think about how they have helped you to develop the skills required for the CanMEDS roles. For each role, identify one or two experiences that you have had that have helped you to develop those skills. Don’t forget to include experiences from outside of healthcare! As we mentioned above, the CanMEDS roles can be demonstrated in a variety of different settings, so don’t limit yourself to only discussing experiences from healthcare.
Finally, think about how you can articulate those experiences in your application. This may include writing about them in your personal statement or discussing them in your interviews. Again, take a look at the detailed description of each CanMEDS role, paying attention to how you have demonstrated exactly what they are looking for in your activities. The key is to be able to effectively communicate how your experiences have genuinely helped you to develop the skills required for the CanMEDS roles.
By following these tips, you will be sure to showcase your skills and qualities in the best light possible, making you a strong applicant for professional school!
Deep Dive into CanMEDS Roles
The following is a full description of the CanMEDS Roles as found on the website for the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada.
Medical Expert
As Medical Experts who provide high-quality, safe, patient-centred care, physicians draw upon an evolving body of knowledge, their clinical skills, and their professional values. They collect and interpret information, make clinical decisions, and carry out diagnostic and therapeutic interventions. They do so within their scope of practice and with an understanding of the limits of their expertise. Their decision-making is informed by best practices and research evidence, and takes into account the patient’s circumstances and preferences as well as the availability of resources. Their clinical practice is up-to-date, ethical, and resource efficient, and is conducted in collaboration with patients and their families, other health care professionals, and the community. The Medical Expert Role is central to the function of physicians and draws on the competencies included in the Intrinsic Roles (Communicator, Collaborator, Leader, Health Advocate, Scholar, and Professional).
Communicator
Physicians enable patient-centred therapeutic communication by exploring the patient’s symptoms, which may be suggestive of disease, and by actively listening to the patient’s experience of his or her illness. Physicians explore the patient’s perspective, including his or her fears, ideas about the illness, feelings about the impact of the illness, and expectations of health care and health care professionals. The physician integrates this knowledge with an understanding of the patient’s context, including socio-economic status, medical history, family history, stage of life, living situation, work or school setting, and other relevant psychological and social issues. Central to a patient-centred approach is shared decision-making: finding common ground with the patient in developing a plan to address his or her medical problems and health goals in a manner that reflects the patient’s needs, values, and preferences. This plan should be informed by evidence and guidelines.
Because illness affects not only patients but also their families, physicians must be able to communicate effectively with everyone involved in the patient’s care.
Collaborator
Collaboration is essential for safe, high-quality, patient-centred care, and involves patients and their families, physicians and other colleagues in the health care professions, community partners, and health system stakeholders.
Collaboration requires relationships based in trust, respect, and shared decision-making among a variety of individuals with complementary skills in multiple settings across the continuum of care. It involves sharing knowledge, perspectives, and responsibilities, and a willingness to learn together. This requires understanding the roles of others, pursuing common goals and outcomes, and managing differences.
Collaboration skills are broadly applicable to activities beyond clinical care, such as administration, education, advocacy, and scholarship.
Leader
The CanMEDS Leader Role describes the engagement of all physicians in shared decision-making for the operation and ongoing evolution of the health care system. As a societal expectation, physicians demonstrate collaborative leadership and management within the health care system. At a system level, physicians contribute to the development and delivery of continuously improving health care and engage with others in working toward this goal. Physicians integrate their personal lives with their clinical, administrative, scholarly, and teaching responsibilities. They function as individual care providers, as members of teams, and as participants and leaders in the health care system locally, regionally, nationally, and globally.
Health Advocacy
Physicians are accountable to society and recognize their duty to contribute to efforts to improve the health and well-being of their patients, their communities, and the broader populations they serve. Physicians possess medical knowledge and abilities that provide unique perspectives on health. Physicians also have privileged access to patients’ accounts of their experience with illness and the health care system.
Scholar
Physicians acquire scholarly abilities to enhance practice and advance health care. Physicians pursue excellence by continually evaluating the processes and outcomes of their daily work, sharing and comparing their work with that of others, and actively seeking feedback in the interest of quality and patient safety. Using multiple ways of learning, they strive to meet the needs of individual patients and their families and of the health care system.
Professional
Physicians serve an essential societal role as professionals dedicated to the health and care of others. Their work requires mastery of the art, science, and practice of medicine. A physician’s professional identity is central to this Role. The Professional Role reflects contemporary society’s expectations of physicians, which include clinical competence, a commitment to ongoing professional development, promotion of the public good, adherence to ethical standards, and values such as integrity, honesty, altruism, humility, respect for diversity, and transparency with respect to potential conflicts of interest. It is also recognized that, to provide optimal patient care, physicians must take responsibility for their own health and well-being and that of their colleagues. Professionalism is the basis of the implicit contract between society and the medical profession, granting the privilege of physician-led regulation with the understanding that physicians are accountable to those served, to society, to their profession, and to themselves.
Closing Thoughts on CanMEDS Framework
Ultimately, the CanMEDS roles provide a comprehensive framework for understanding what it takes to be a successful physician. As such, they should be given due consideration in any professional school application. Adcoms are looking for applicants who have a clear understanding of the roles and responsibilities of physicians. By demonstrating an awareness of the CanMEDS roles in your application, you can show that you have the necessary foundation to be a successful physician.
The CanMEDS roles are just one part of becoming a strong applicant for professional school applications. Be sure to understand the requirements for medical schools (or requirements for dental schools), as well as the MCAT sections, and MMI/Panel Interview Prep Resources. Good luck on your application!
About the Author
Hi, my name is Jack Rzepka, founder of Masterstudent.ca. I graduated from McMaster University’s Bachelor of Health Sciences (BHSc) program in 2021, and I was fortunate to be accepted to multiple Canadian dental and medical schools, including the University of Toronto Faculty of Dentistry and the University of Western Ontario Schulich School of Medicine.
I know firsthand how stressful applying to graduate and professional programs can be. I was juggling multiple applications, trying to figure out where to find accurate information, and worrying about how expensive DAT and MCAT prep could really be. I created Masterstudent.ca because I remember how overwhelming it felt to piece together guidance from scattered sources. My goal is to give students a clear, reliable, and student-focused resource, so you can make informed decisions without feeling lost or alone. We have practice tests, guides to applications, and articles on studying tips and the like all made free during my spare time (and it will always be free).
Navigating applications is challenging, but I don’t want you to have to do it by yourself. That’s why I’m here to share what I’ve learned and help you make the process a little less stressful.
